How To Answer a Kentucky Debt Collection Court Summons
Upsolve is a nonprofit that helps you eliminate your debt with our free bankruptcy filing tool. Think TurboTax for bankruptcy. You could be debt-free in as little as 4 months. Featured in Forbes 4x and funded by institutions like Harvard University — so we’ll never ask you for a credit card. See if you qualify
If you are sued for debt in Kentucky, the best thing you can do is respond and take action! If you are sued through circuit court or district court (not small claims), you need to file an answer within 20 days of receiving your summons and complaint. If you are sued through the small claims division of the district court, you don’t have to file an answer but you can file a counterclaim. Local rules vary from county to county, so it’s always best to check with your court to verify the best way to proceed with your case.
Written by Attorney Tina Tran. Legally reviewed by Jonathan Petts
Updated May 5, 2025
Table of Contents
How Do Debt Collection Lawsuits in Kentucky Work?
32% of Kentuckians have at least one debt in collection, which is higher than the national average (26%). So if you're struggling with debt, you aren't alone. If phone calls and notices in the mail don't work, the debt collector may decide to bring a debt collection lawsuit against you.
In Kentucky, debt collection lawsuits are handled in either a district court or circuit court:
Circuit courts are general jurisdiction courts that hear civil cases dealing with suits filed for more than $5,000.
District courts hear civil cases dealing with debt amounts of $5,000 and below, with a small claims division that handles cases involving $2,500 or less.
All circuit and district courts in Kentucky have their own local rules. This article is designed to provide general guidance and information, so it’s important to read your court paperwork carefully to identify which court is hearing your case. Regardless of where your case is heard, you’ll receive two forms to notify you that a debt collection lawsuit has been filed against you — a summons and complaint.
What Is a Summons and Complaint?
A summons and complaint are official court documents you’ll receive if you’re being sued for unpaid debt.
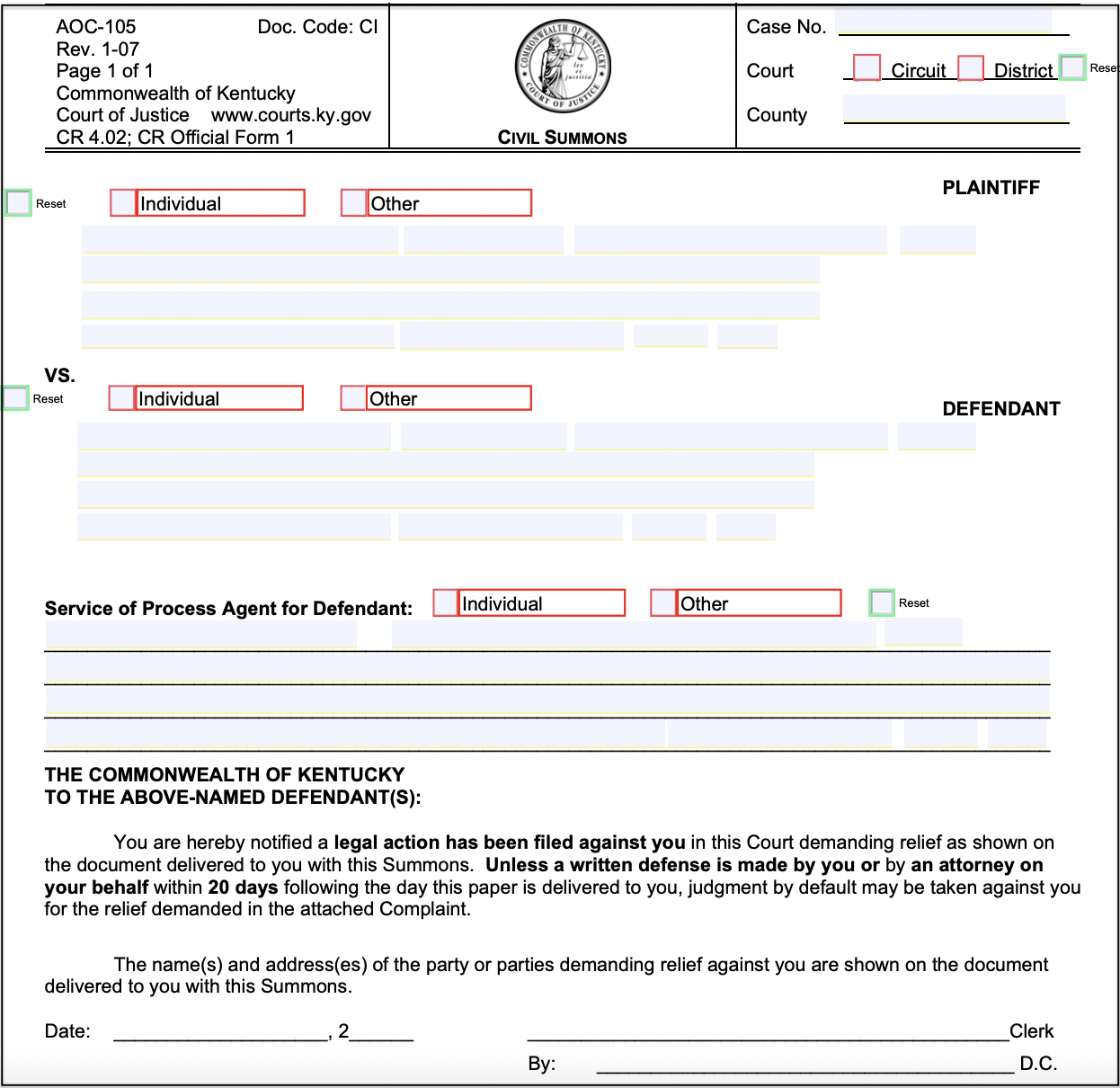
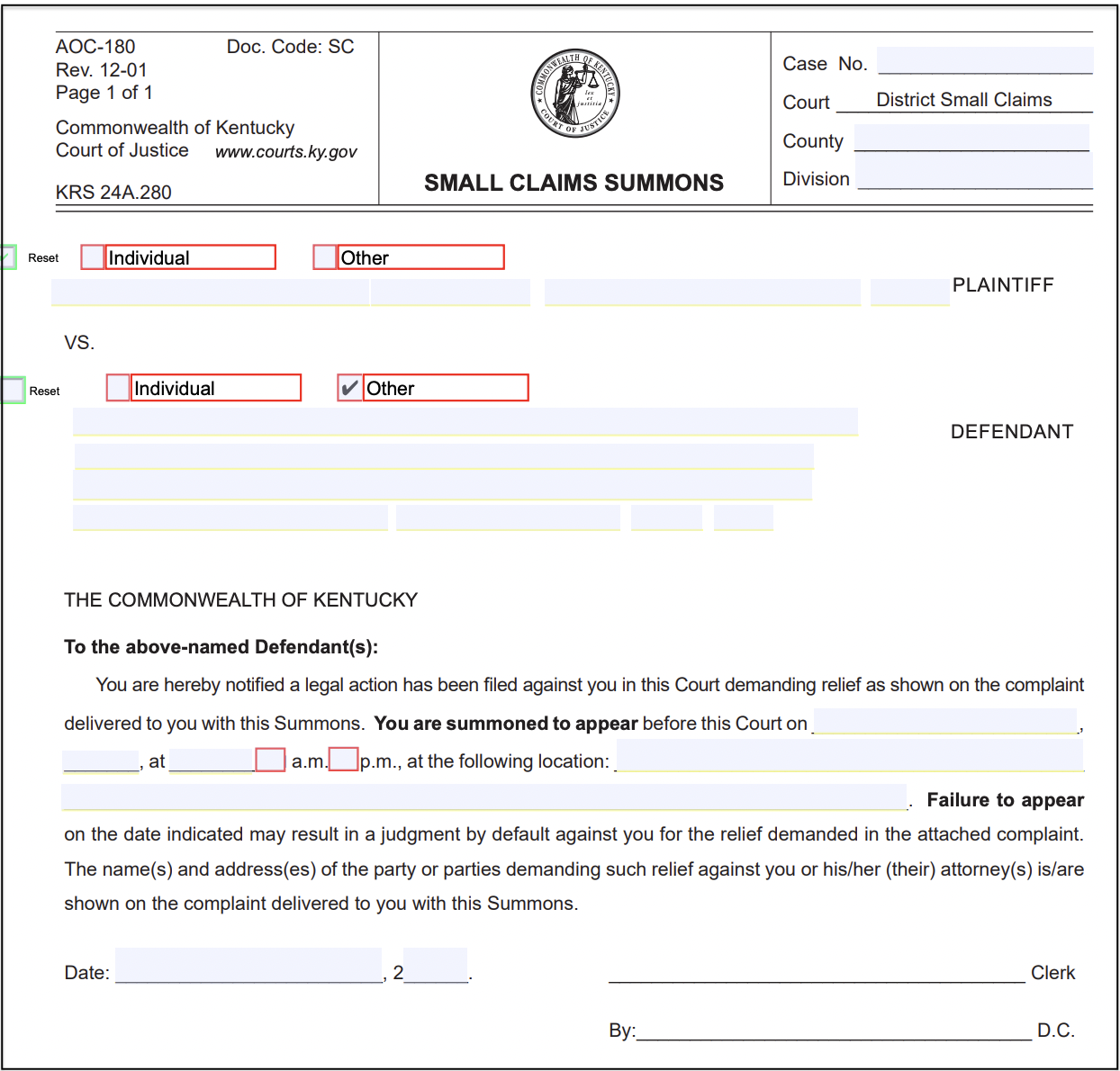
The summons is a court document notifying you that a lawsuit has been filed against you. The summons will tell you the deadline to respond to the complaint and which court will hear your case. In a small claims case, the summons will include a hearing date, time, and place.
The complaint outlines the allegations, or claims, that the plaintiff is making against you. The plaintiff is the legal term for the person who’s suing you. In a debt collection lawsuit, the complaint will list claims about your debt, such as how much the collector thinks you owe and why they believe you owe it.
The complaint will also explain what the debt collector wants from the lawsuit. Usually, they are looking for a court-ordered money judgment to collect the debt. The judgment amount could include the debt the collector believes you owe, interest accrued since your last payment, and any other costs the plaintiff thinks you should cover, such as legal costs.
A summons in Kentucky looks like this:
A summons from the small claims division of a district court in Kentucky looks like this:
How Do You Respond to a Kentucky Court Summons for Debt Collection?
If your case is filed in circuit court or district court (not small claims), you need to file an answer form within 20 days after you receive the summons.If you don’t, you could lose the case automatically. Your answer must include any affirmative defenses or counterclaims you have (more on this below).
If your case is being handled by the small claims division of the district court in your county, you don’t have to file a written answer to defend your case. Instead, you must show up on your scheduled court date and bring evidence to present your defense. Your summons will have your hearing date and time on it.
Note: Even if your case is with a small claims court and you’re not filing an answer form, it’s important to keep reading so you understand how to prepare your defense for your court date.
📌 If you want help responding to the debt lawsuit but you can't afford a lawyer, consider using SoloSuit, a trusted Upsolve partner. SoloSuit has helped 280,000 respond to debt lawsuits and settle debts for less. They have a 100% money-back guarantee, and can make the response process less stressful and quicker!
How Do You Fill Out an Answer Form?
You will need to file an answer form with your court if your case is in circuit or district court (not small claims). The answer form is your chance to explain your side of the lawsuit and present any defenses you have.
The Appalachian Research and Defense Fund of Kentucky has a very helpful sample answer form with instructions on how to fill out and file your answer.
Here is what the first page of the answer form looks like:

Step 1: Address Each Complaint/Allegation
In the “Responses” section of the answer form, address each claim from the complaint. Be sure to address every allegation.
You can respond to an allegation by:
Admitting it, which means you admit that the statement is true
Denying it, which means you deny that the statement is true. If only part of the statement is true, the safest bet is usually to deny the entire statement.
Claiming a lack of knowledge of the truth, which means you don’t know if the statement is true or not without more information
On the complaint, each allegation will be numbered. Make sure your responses address and match up with the numbered paragraphs on the complaint.
Step 2: Raise Your Affirmative Defenses
In the next section of the answer form, there’s space to write any affirmative defenses you may have.
You’re required to list specific legal reasons — the affirmative defenses — why you should not be held responsible for the claims made against you in the complaint.
This is what the affirmative defense section of the answer form looks like:

Though the form lists several affirmative defenses, many are technical-sounding legal terms. It’s okay for you to write your affirmative defense in layman’s terms in the space provided.
Here’s some of the more common affirmative defenses used in debt collection lawsuits:
Statute of limitations: This is a way of saying the debt is too old for the debt collector to sue you for it. The statute of limitations in Kentucky for credit card and medical debt is usually 5–10 years.
Discharge in bankruptcy: If the debt you’re being sued for is part of a bankruptcy filing, this affirmative defense could apply. Debt collectors are not supposed to contact you or pursue any collection measures after you file bankruptcy on that debt.
Payment: If you don’t believe you owe the debt because you already paid it off, you can use this as an affirmative defense. Be prepared to show the court proof of payment.
Mistaken identity: If the debt isn’t yours, you can use this as an affirmative defense.
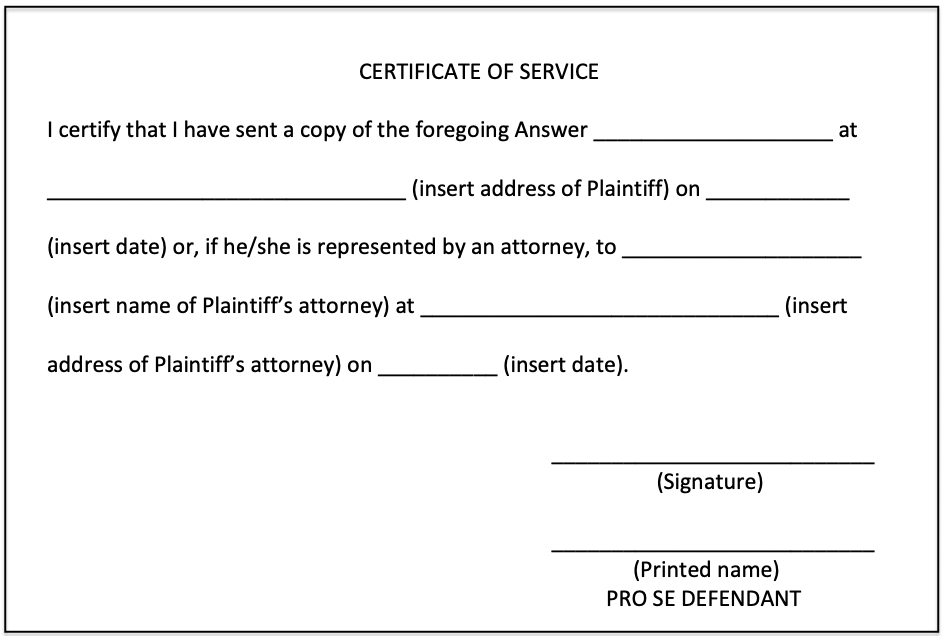
Step 3: Complete the Certificate of Service
You are required to serve your answer form on the plaintiff. Serving your answer just means sending a copy in a way that complies with court rules. Sending a copy to the plaintiff lets them know you're responding to their claims. Sometimes this is enough to get the plaintiff to drop the lawsuit altogether.
To prove to the court that you have responded to the plaintiff directly, you will fill out the certificate of service section of the answer form.
You can mail the plaintiff’s (or their attorney if they have one) copy to them. It’s best to use certified mail with a return receipt so you have proof of the mailing.
The certificate of service section of the answer form for Kentucky looks like this:
Step 4: File Your Forms With the Court Clerk Within 20 Days
After you fill out your answer form, you need to make two copies. File the original form with the court, send one to the plaintiff, and keep one for your records.
You have to file your answer with the court listed on the summons within 20 days of receiving the summons.
The rules for filing your form with the court are different from the rules for serving your form on the plaintiff (or their attorney). Many people file their answer in person at the court clerk’s office. Make sure to ask the clerk for a copy of the stamped forms, again to keep for your records. You can also e-file with KYeCourts — the main eCourt page has information on how to e-file your case. You may be able to mail your answer form to the court as well. Call the court clerk to ask if this is allowed.
What Happens After You Respond to the Lawsuit?
The rules and procedures differ by county in Kentucky. Some circuit court judges may require mediation prior to (or in lieu of) a trial. You can check the local rules or speak with the court clerk to ask about what usually happens after people file an answer form.
How To Prepare for Court Appearances
It’s normal to feel intimidated or overwhelmed when dealing with the court system. Spending a little time preparing for your appearance and following some simple best practices can help make the situation feel more manageable.
The best practices to follow for a successful court appearance include:
Arriving early for your hearing
Speaking respectfully to the judge and other people in the courtroom
Dressing professionally
Being organized and bringing copies of relevant documents to support your defenses
Upsolve’s article on What Happens In Small Claims Court has other helpful tips.
What Happens if You Don’t Respond to the Lawsuit?
The most important thing you can do in a debt lawsuit is acknowledge it and take action. If you ignore the lawsuit, it won’t just go away. Instead, you’re likely to lose the case and have a default judgment issued against you. This allows the person or company suing you to request a court order for wage garnishment, a bank account levy, or a property lien.
Debt collectors count on you not attending court or responding to the lawsuit. If you take action and respond to the lawsuit, you give yourself a fighting chance to win the debt collection lawsuit. As mentioned above, sometimes simply responding to the lawsuit is enough to get the person suing you to drop the case. Remember: They want an easy win. Don’t make it easy for them.
What Do I Do if the Court Already Issued a Default Judgment Against Me?
If a default judgment has already been ordered against you, you can file a motion to vacate the judgment. To vacate means to cancel the judgment ordered. The court may grant the motion if there’s “good cause” — good cause means there’s a valid and justifiable reason for the judgment to be ordered against you.
Filing this motion simply means submitting a formal request (usually via a form) to the court. You can always speak to the court clerk at the court where your case has been assigned to tell them your situation and ask about your options. While clerks can’t give legal advice, they should be able to tell you if there’s a process in place to contest the judgment. If you want to pursue vacating the judgment, it’s a good idea to take advantage of the resources in the following section and possibly seek legal help
Need Legal Help?
Legal Self-Help - Kentucky Court of Justice has self-help guides and online resources with links to local and statewide resources.
Small Claims Handbook details a citizen’s guide to navigating a small claims complaint in Kentucky.
Kentucky Court of Justice has information on the courts throughout the state, legal self-help guides, and information on court programs.
